@[TOC](Pytorch torch.nn库以及nn与nn.functional有什么区别?)
微信公众号:数学建模与人工智能
tocrch.nn库
torch.nn是专门为神经网络设计的模块化接口nn构建于autograd之上,可以用来定义和运行神经网络
nn.Parameter
nn.Linear&nn.conv2d等等
nn.functional
nn.Module
nn.Sequentialnn.Parameter
- 定义可训练参数
- self.my_param=nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1))
- self.register_parameter
- nn.ParameterList&nn.ParameterDict
这个类实际上是将一个Parameter的List转为ParameterList,如下例所示[nn.Parameter(torch.randn(10, 10)) for i in range(10)]类型是List,List的每个元素是Parameter,然后这个List作为参数传入这个类构造ParameterList类型。 ParameterList输入一定是一个Parameter的List,其他类型会报错,在注册时候就会提示元素不是Parameter类型。
self.params = nn.ParameterList([nn.Parameter(torch.randn(10, 10)) for i in range(10)])输入参数是个普通字典,然后转换为ParameterDict类型。
self.params = nn.ParameterDict({
'left': nn.Parameter(torch.randn(5, 10)),
'right': nn.Parameter(torch.randn(5, 10))
})nn.Linear&nn.conv2d&nn.ReLU&nn.maxPool2d&nn.MSELoss等等
各种神经网络层的定义,继承于nn.Module的子类
- self.conv1=nn.Conv2d(1,6(5,5))
- 调用时:slef.conv1(x)
参数为parameter类型
- layer=nn.Linear(1,1)
- layer.weight=nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor([[0]]))
- layer.bias=nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor([0]))
nn.functional
包含torch.nn库中所有函数,包含大量loss和activation function
- torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input,weight,bias=None,stride=1,padding=0,dilation=1,groups=1)
- 没有学习参数的(eg.maxpool,loss_func,activation func)等根据个人选择使用nn.functional.xxx或nn.xxx
- 关于dropout层,推荐使用nn.xxx。因为一般情况下只有训练时才用dropout,在eval不需要dropout。使用nn.Dropout,在调用model.eval()后,模型的dropout层都关闭,但用nn.functional.dropout,在调用model.eval()后不会关闭dropout.
nn与nn.functional有什么区别?
- nn.functional.xxx是函数接口,而nn.Xxx是nn.functional.xxx的类封装,并且nn.Xxx都继承于一个共同祖先nn.Module。
- nn.Xxx除了具有nn.functional.xxx功能之外,内部附带了nn.Module相关的属性和方法,例如train(), eval(),load_state_dict, state_dict等。
- 两者的调用方式不同。nn.Xxx 需要先实例化并传入参数,然后以函数调用的方式调用实例化的对象并传入输入数据。nn.functional.xxx同时传入输入数据和weight, bias等其他参数 。
- nn.Xxx继承于nn.Module, 能够很好的与nn.Sequential结合使用, 而nn.functional.xxx无法与nn.Sequential结合使用
- nn.Xxx不需要你自己定义和管理weight;而nn.functional.xxx需要你自己定义weight,每次调用的时候都需要手动传入weight, 不利于代码复用。
nn.Sequential
一个有序的容器,神经网络模块将按照在传入构造器的顺序依次被添加到计算图中执行,同时以神经网络模块为元素的有序字典也可以作为传入参数
# Example of using Sequential
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1,20,5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(20,64,5),
nn.ReLU()
)
# Example of using Sequential with OrderedDict
model = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv1', nn.Conv2d(1,20,5)),
('relu1', nn.ReLU()),
('conv2', nn.Conv2d(20,64,5)),
('relu2', nn.ReLU())
]))nn.ModuleList
它可以以列表的形式来保持多个子模块。
ModuleList能够像python列表一样被索引访问,而且其中的模块会被正确地登记注册,而且它保存的模块可以被所有Module方法可见,之所以不能直接用python列表来保存,是因为PyTorch需要自动跟踪计算图并计算自动梯度,如果直接使用python列表或者python字典来保存module,那么无法正确地自动计算梯度.
class MyModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModule, self).__init__()
self.linears = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(10, 10) for i in range(10)])
def forward(self, x):
# ModuleList can act as an iterable, or be indexed using ints
for i, l in enumerate(self.linears):
x = self.linears[i // 2](x) + l(x)
return xnn.ModuleDict
class MyModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModule, self).__init__()
self.choices = nn.ModuleDict({
'conv': nn.Conv2d(10, 10, 3),
'pool': nn.MaxPool2d(3)
})
self.activations = nn.ModuleDict([
['lrelu', nn.LeakyReLU()],
['prelu', nn.PReLU()]
])
def forward(self, x, choice, act):
x = self.choices[choice](x)
x = self.activations[act](x)
return xnn.Module
它是一个抽象概念,既可以表示神经网络中的某个层(layer),也可以表示一个包含很多层的神经网络
model.parameters()
model.buffers()
model.state_dict()
model.modules() 迭代遍历模型的所有子层,所有子层即指nn.Module子类
forward(),to()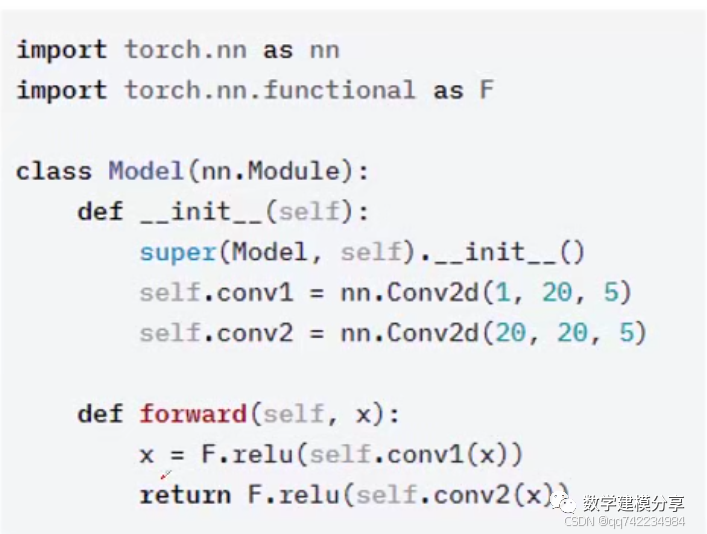
Parameters VS buffers
一种是反向传播需要被optimizer更新的,称之为 parameter(如权重等)
- self.register_parameter("param",param)
- self.param=nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1)) 一种是反向传播不需要被optimizer更新,称之为 buffer(一些阈值之类的)
- self.register_buffer(''my_buffer,torch.randn(1))
模型状态字典 state_dict() & load_state_dict
1、state_dict() 返回一个包含 Module 实例完整状态的字典,包括参数和缓冲区,字典的键值是参数或缓冲区的名称 2、load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=True) 从 state_dict 中复制参数和缓冲区到 Module 及其子类中
- state_dict:包含参数和缓冲区的 Module 状态字典
- strict:默认 True,是否严格匹配 state_dict 的键值和 Module.state_dict()的键值
torch.save(obj=model.state_dict().f="modles/net.pth")
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("models/net.pth"))